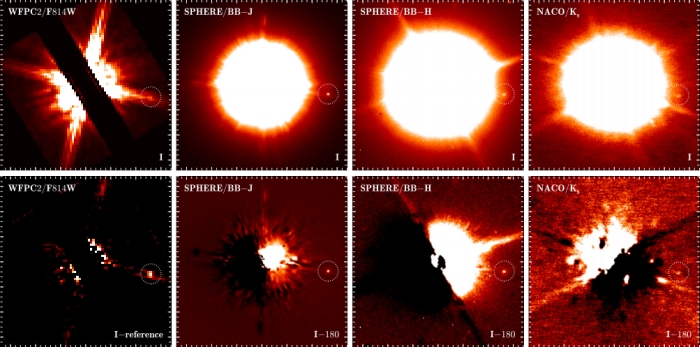
Sometimes the most amazing discoveries can happen just by chance. Case in point: an international team of astronomers accidentally photographed what they think is a planet in the process of growing bigger, 600 light-years away. The star in question is a binary called CS Cha, located in a star-forming region in the southern constellation of Chamaeleon.
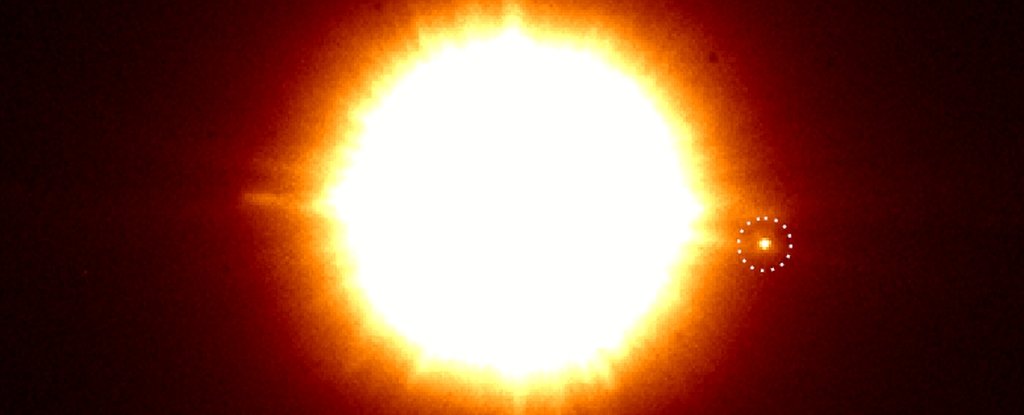
CS Cha has what is known as a circumbinary disc, which surrounds both stars in the binary system. But when they were looking at the images, the researchers saw a small dot of light near the binary, outside the circumbinary disc. When they looked at images taken by the VLT’s NACO instrument 11 years ago, they saw the dot again.
And again in photos taken by the Hubble Space Telescope’s Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 19 years ago. So it wasn’t a glitch, or a transient anomaly – it was something that was really there persistently over time and it was moving with CS Cha – it’s definitely a companion to the binary star. Now, the researchers don’t know with certainty what it is, yet. The options are relatively limited for a visible object orbiting a star.
It could be a brown dwarf, a type of very low mass “failed” star too small to sustain hydrogen fusion, but too big and too hot to be categorised as a gas giant. It could, however, also be a large gas giant that’s still growing, what is referred to as a super-Jupiter.
Spectroscopic analysis to try and figure out which has proven difficult, but the reason why has the research team intrigued.
“The most exciting part is that the light of the companion is highly polarised. Such a preference in the direction of polarisation usually occurs when light is scattered along the way,” explained astronomer Christian Ginski of Leiden University, lead author on the new paper. “We suspect that the companion is surrounded by his own dust disc. The tricky part is that the disc blocks a large part of the light and that is why we can hardly determine the mass of the companion. So it could be a brown dwarf but also a super-Jupiter in his toddler years. The classical planet-forming-models can’t help us.”
If it’s either of one of those two things, the find will be an extraordinary one. Most exoplanets are too far away to be photographed directly.
Infographic of the binary star CS Cha and its surrounding dust disc (left) with the newly discovered companion (right). The companion is located at more than 214 times the distance earth-sun fromthe binary, but clearly belongs to the system. The whole system is about 165 parsec (538 light years) away from Earth. Credit: C. Ginski/G.A. Muro Arena
Read more at: https://phys.org/news/2018-05-dutch-astronomers-toddler-planet-chance.html#jCp
“Brown dwarf companions to solar-type stars are extremely rare,” researcher Michael McElwain of Princeton University told Space.com at the time.
“The CS Cha system is the only system in which a circumplanetary disc is likely present as well as a resolved circumstellar disc. It is also to the best of our knowledge the first circumplanetary disk directly detected around a sub-stellar companion in polarised light, constraining its geometry,” the researchers wrote in their paper. “Once the system is well understood it might be considered a benchmark system for planet and brown dwarf formation scenarios.”